
ĪMNIOTIC FLUID Composition and volume of amniotic fluid changes as pregnancy advances In the first half of pregnancy, the fluid is the same as the extracellular fluid of the fetus, devoid of particulate matter Produced by amniotic membranes Fluid also passes across fetal skin ĪMNIOTIC FLUID By the fourth month, the fetus contributes to amniotic fluid via: urinating swallowing movement of fluid in and out of the respiratory tract Fetal urination will eventually comprise the majority of the amniotic fluid ĪMNIOTIC FLUID The fetal kidneys start to develop during the 4th and 5th weeks of gestation and begin to excrete urine into the amniotic fluid at the 8th to 11th week At the 20th week the fetal kidneys produce most of the amniotic fluid Fetal urine is hypotonic (c/w plasma) because of lower electrolyte concentration Contains more urea, creatinine and uric acid Osmolality decrease with increasing gestational age ĪMNIOTIC FLUID An important function of the fetal kidney is to maintain a urine output sufficient to maintain amniotic fluid volume Daily urine production is approximately 30% of fetal weight The excreted urine does not serve real excretory or homeostatic function because the urine, via the amniotic fluid, is recycled back to the fetus by swallowing (25% of fetal weight) ĪMNIOTIC FLUID The factors involved in regulating amniotic fluid volume are still not completely understood.

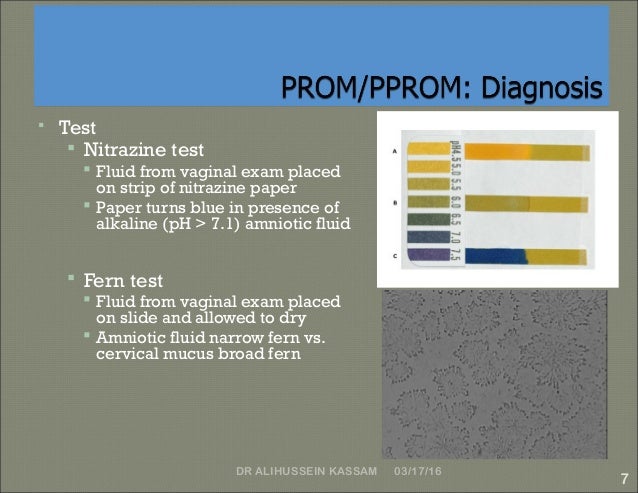
#Amniotic fluid infection full#
50 ml 12 weeks 400 ml midpregnancy 800 ml 34 weeks 1000ml 36-38 weeks At full term, there is between 500-1000 cc of amniotic fluid. It cushions the fetus from physical trauma Provides a barrier against infection Allowing for freedom of fetal movement and permitting symmetrical musculoskeletal development Maintaining a relatively constant temperature for the environment surrounding the fetus, thus protecting the fetus from heat loss Permitting proper lung development ĪMNIOTIC FLUID Cleavage of zygote Zygote begins cleavage in the fallopian tube s/p 3 days in the fallopian tube, the morula enters uterine cavity After 3 days floating in the uterine cavity it will implant Gradual accumulation of fluid between blastomeres within the morula results in the formation of the blastocyst Inner cell mass-embryo Outer cell mass-trophoblast ĪMNIOTIC FLUID 7 1/2 days: Trophoblast Cytotrophoblast: individual, pale staining cells Syncytiotrophoblast: dark staining nuclei within an amorphous common cytoplasm Inner cell mass: embryonic disc thick ectoderm and underlying endoderm Between the embryonic disc and the trophoblast, small cells appear that enclose a space that will become the amniotic cavity ĪMNIOTIC FLUID Small cells line the inner surface of the trophoblast called amniogenic cells, later to become amniotic epithelium The amnion develops by the 7-8 th day Derived from fetal ectoderm As the amnion enlarges, it gradually engulfs the embryo which prolapses into its cavity Distention of the amniotic sac brings it in contact with the chorion laeve The chorion and amnion are juxtaposed but not connected ĪMNIOTIC FLUID Clear fluid collects within the amniotic cavity and increases with gestational age.
AMNIOTIC FLUID By La Lura White MD Maternal Fetal MedicineĪMNIOTIC FLUID The amniotic fluid that bathes the fetus is necessary for its proper growth and development.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
