
We can calculate the acceleration shown in the first section of the green line as follows: = change in velocity (m/s) ÷ time taken (s) The acceleration shown in the purple line can be calculated as follows: The units of acceleration are m/s/s or m/s 2. Notice that a line sloping downwards - with a negative gradient - represents an object with a constant deceleration (it is slowing down).Īcceleration can be calculated by dividing the change in velocity (measured in metres per second) by the time taken for the change (in seconds). The purple line is steeper than the green line because it represents an object with a greater acceleration. The steeper the line, the greater the acceleration of the object. The diagram shows some typical lines on a velocity-time graph. When an object is undergoing constant acceleration, the line on the graph is straight but sloped.Ĭurved lines on velocity-time graphs also show changes in velocity, but not with a constant acceleration or deceleration.
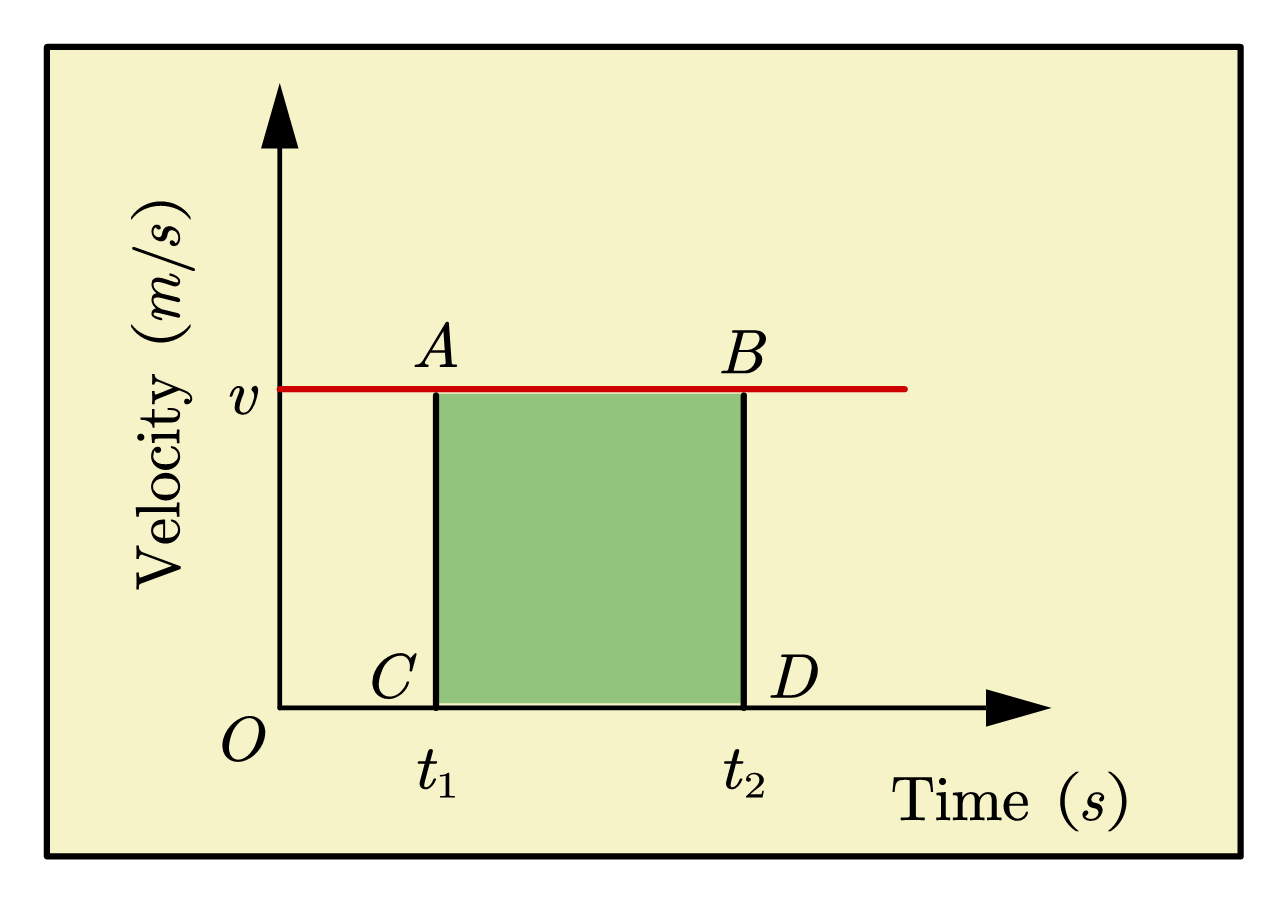
When the horizontal line is at zero velocity, the object is at rest. When an object is moving with a constant velocity, the line on the graph is horizontal. The horizontal axis is the time from the start.

The vertical axis of a velocity-time graph is the velocity of the object. Velocity-time graphs are also called speed-time graphs. Two cars travelling at the same speed but in opposite directions have different velocities.Ī velocity-time graph shows the speed and direction an object travels over a specific period of time.

The velocity of an object is its speed in a particular direction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
